Older publications here ...
Book chapters here...
New papers from us

Hybrid speciation in the Amazon. Rosser, N., Seixas, F.et al. 2024. Hybrid speciation driven by multilocus introgression of ecological traits. Nature 628:811-817. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07263-w

Halloween cover of PNAS, 31 October 2023. Tianzhu Xiong, et al. Hybrid sterility in female butterflies is best explained by a polygenic model of inheritance on Z chromosome and autosomes.

Cover of Science, Nov. 1, 2019.
The issue features our paper on genomic evidence for gene flow among species. Photo by Andrew Neild.
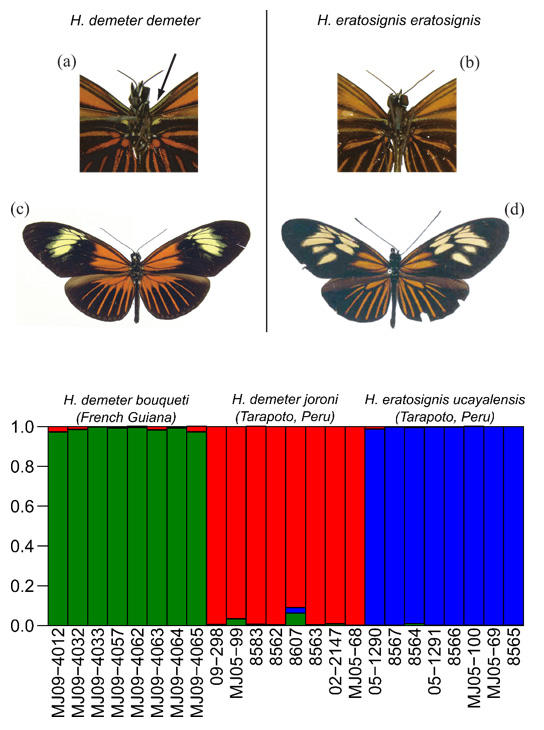
A cryptic species discovered in Heliconius ! It is not always the case that mtDNA 'barcode' differences correctly delimit separate species. However, we recently found two cryptic Heliconius species that co-occur in sympatry in a narrow zone of overlap in Amazonia, initially via barcoding. Furthermore, the two taxa are co-mimics, so no mimicry switch led to speciation here, although we had thought that mimicry switches typically accompanied speciation in the genus Heliconius. Rosser et al. 2019.
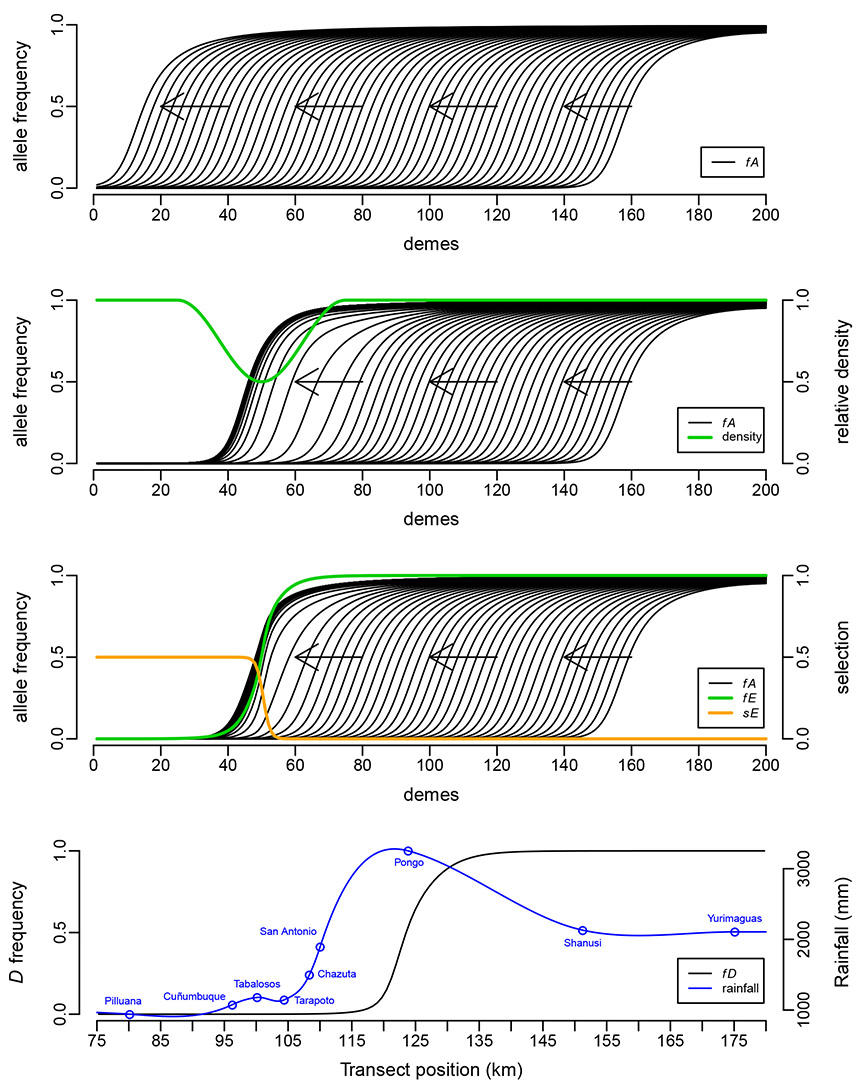
What prevents hybrid zones from moving? (a), top above. Could be there's a density trough (b), or a cline at another ecologically relevant locus that interferes (c)? We argue that it's more likely that a high rainfall peak (d), bottom at the edge of the Andes traps butterfly hybrid zones, to form a massive suture zone in many butterfly taxa. (See Rosser et al. 2014).
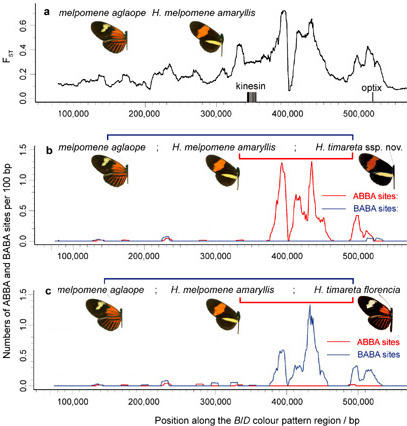
Evidence for adaptive introgression at the B/D mimicry locus
a, Genetic divergence between H. melpomene races aglaope (rayed) and amaryllis (postman) across a hybrid zone in northeast Peru. Divergence, FST, measured along the B/D genomic region peaks in the locus that controls red wing pattern elements between the genes kinesin and optix. b, c, Distribution of fixed ABBA and BABA sites (see above) along B/Dregion for two comparisons between H. melpomene and H. timareta. Excesses of ABBA in b and BABA in c are highly significant, indicating introgression of colour pattern control region. From Fig. 4 of Heliconius Genome Consortium 2012
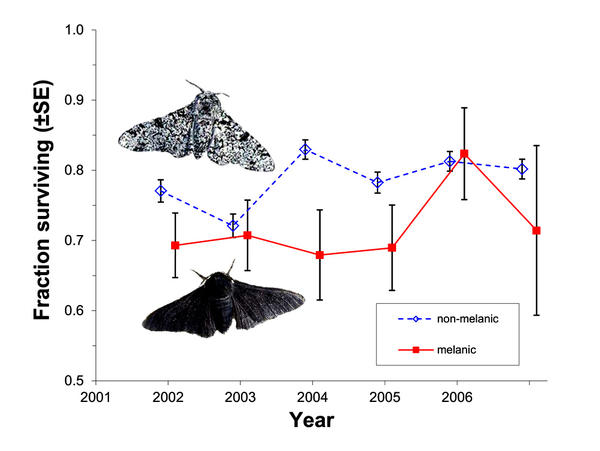 Selection against melanism in UK after the Clean Air Act. Survival of peppered moth morphs (+/- SE) over the course of six years of the predation experiment. Unfilled diamonds with dashed lines, non-melanic; filled squares with solid lines, melanic. From Fig. 1 of Laurence Cook et al. 2012
Selection against melanism in UK after the Clean Air Act. Survival of peppered moth morphs (+/- SE) over the course of six years of the predation experiment. Unfilled diamonds with dashed lines, non-melanic; filled squares with solid lines, melanic. From Fig. 1 of Laurence Cook et al. 2012